Cardiac Drones: Emergency Drone Delivery for Cardiac Patients using Smart Watch
Written by Priyanka Dey on 23.02.2023
The advancement of AI and wearable IOT has revolutionize the area of medical diagnostics, especially diagnostics of cardiac arrhythmia. Instead of long-time and expensive conventional method, now-a-days, smart wearable devices (smart-watch, smart textile etc.) are used widely for heart rate monitoring due to their portability and ease of use.
Additionally, machine learning (ML) based predictive models are also being used over smart-wearable data to create - early warning systems, i.e., continuous heart monitors and many more useful medical interfaces. Having cloud frameworks [1] as backbone, these smart systems have granted access to large amount of personal health data for better diagnostics and treatment [2]. In this article, I describe a bird-eye-view of an emergency medical drone delivery system that uses smart wearable (smart watch) and a mobile app to trigger an emergency flight. This project is an ongoing effort under Med4PAN that delivers emergency medical drone service to users/patients with a cardiac emergency.
All drones under this service are equipped with necessary hardware (e.g., Ardupilot /pixhawk2.1), Raspberry-pi systems, batteries, sensors and GPS receivers, internet module for automated drone delivery [3].
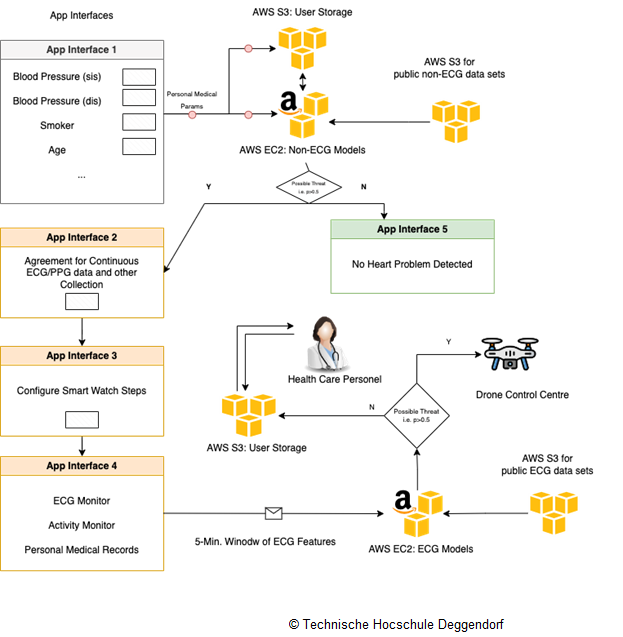
The drones are also equipped with Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs). AEDs are portable electronic devices that can diagnose and treat life-threatening heart conditions in emergency situations. Smart watches are used to trigger the dispatch of such AED equipped drones. When a smart watch detects a potential anomaly in heart rate, considering other medical (user’s personal medical data) and situational (user's state i.e., walking, running, resting) parameters, it automatically sends an alert to emergency drone services with user's live location.
Upon receiving the alert, a drone, pre-configured with AED, flies to the destination (i.e. user's live location). There are three major components of smart watch based cardiac threat detection system - (i) an offline process, which is followed to create ML models from publicly available data sets; (ii) a mobile app, which continuously gathers user's medical (ECG, PPG , clinical parameters) [4] [5] and situational (user's state, routine) data using pre-built smart watch sensors; (iii) prediction stream from models [6] (trained during offline process) on user's data which is monitored continuously for potential alert. Further to that, all the data handled by the framework are stored in a cloud-based platform (AWS) for future reuse and analysis. As an additional sub case, these drones can also be equipped with cameras and other hardware to facilitate remote consultations between doctors and patients. This can be particularly useful for patients in rural areas who may not have easy access to medical specialists. This use case has a potential to significantly impact the public health care in a positive way by improving the response time of Emergency Medical Response Service (EMRS) for health care institutions.
Figure 1: Cardiac diagnosis framework with cloud, user and app interfaces
References:
[1] Yang, Z. a. (2016). An IoT-cloud based wearable ECG monitoring system for smart healthcare. Springer, 1--11.
[2] Duncker, D. a. (2021). Smart wearables for cardiac monitoring—real-world use beyond atrial fibrillation. MDPI, 2539.
[3] https://ardupilot.org/copter/index.html
[4] Ribeiro, H. D.-S. (2022). ECG-based real-time arrhythmia monitoring using quantized deep neural networks: A feasibility study. Elsevier, 105249.
[5] Ghosh, P. a. (2021). Efficient prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning algorithms with relief and LASSO feature selection techniques. IEEE, 19304--19326.
[6] Subahi, A. F. (2022). Modified Self-Adaptive Bayesian Algorithm for Smart Heart Disease Prediction in IoT System. MDPI, 14208.